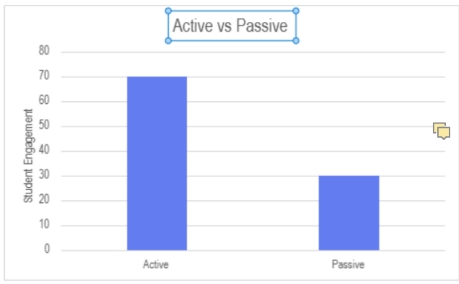
Research Question: How do passive vs active learning strategies affect student engagement on water conservation education?
Review Paper 1
- Team member evaluation:
Sonia Sheryr - Citation for the article:
Siripoulos, Costas and Pomonis, Gerasimos. “Alternatives to ‘Chalk and Talk’:
Active Vs. Passive Learning – A Literature Review of the Debate”. SSRN, 3 April 2007. Alternatives to ‘Chalk and Talk’: Active Vs. Passive Learning – A Literature Review of the Debate by Costas Siriopoulos, Gerasimos A. Pomonis :: SSRN - 1-paragraph summary:
Using over 20 different sources to collect data, Siripoulos and Pomonis develop four different hypotheses on the advantages of learning strategies in college courses. Each hypothesis they come up with pits “lecture learning” against a different teaching method. At the end of their research, they
discovered that the majority of the authors they had looked into supported either hybrid or active learning. For the first hypothesis, all of their sources argued that lecture methods were outdated and needed to be replaced by hybrid methods. The same results panned out for the second hypothesis, with all of the sources agreeing that active learning was better for student understanding than lecture learning. For the use of case study methods, only 25 out of 40 sources supported their adoption, due to the fact that it could
lead to students adopting passive learning styles if taught wrong. Long distance learning over lecture learning was only supported by 13 out of 40 sources since it does not have any major effects on student learning. - What information does this source contribute to your research question?
This source supports the idea that lecture methods are not good enough to teach advanced courses to students. Some implementation of active learning strategies are essential to teach many college level courses. - How does the source relate to other sources in your bibliography?
Ultimately, hybrid strategies are praised the most, just like in most of the other sources. - What are the strengths and weaknesses of the source? While the authors’ use of 40 sources does make the results more significant, these results only apply to college level courses, leaving out any information on the effects of active learning on students of younger ages.
- How does the source fit into your research topic? Why is it useful?
This source provides an argument for active learning being more helpful for a student’s education than passive learning.
Review Paper 2
- Team member evaluation:
Jaiden DeBoe - Citation for the article
Gamo, Joel. “Anatomy Education-Paradigm Shift from Passive to Active Learning-Effects on Student Engagement, Comprehension and Retention A Review of Literature from 2012 to 2022”. The FASEB Journal, 13 May 2022, vol. 36, issue S1. Anatomy Education‐Paradigm Shift from Passive to Active Learning‐Effects on Student Engagement, Comprehension and Retention A Review of Literature from 2012 to 2022 – Gamo – 2022 – The FASEB Journal – Wiley Online Library - 1-paragraph summary:
In order to determine the true advantages of active learning over passive learning, Gamo analyzes studies conducted on the subject from 2012 to 2022. Most of the studies come back to the same conclusion, that active learning allows for better student engagement, comprehension, and retention. In fact, the National Training Laboratories in Maine provided a statistic which states that passive learning, on average, leads to a 30% retention rate, while active learning leads to retention rates of 50%-90%. This is because active learning strategies force the students to seek out information on their own, while passive learning strategies simply force feed a lot of knowledge to the students, leaving many of them disinterested. - What information does this source contribute to your research question?
This source not only shows how active teaching is more effective in a student’s education, but also offers reasons why this is the case, such as comprehension and retention. - How does the source relate to other sources in your bibliography?
Similar to the first source, the studies used in this article also come from college level classes. - What are the strengths and weaknesses of the source?
This article does a great job at explaining why people believe active learning is better than passive learning. However, Gamo does not mention what specific sources had to say about the topic, instead opting to summarize what the majority of his sources agreed upon. - How does the source fit into your research topic? Why is it useful?
Gamo is able to show real results for the switch from passive learning to active learning instead of just claiming that one is better than the other.
Research Paper 1
- Team member evaluation:
Sonia Sheryr - Citation for the article
Munna, A. S., and Kalam, M. A. “Impact of Active Learning Strategy on the Student Engagement”. GNOSI: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Human Theory and Praxis, vol. 4, no. 2, Apr. 2021, pp. 96-114. ED614302.pdf - 1-paragraph summary:
Munna and Kalam were curious as to why student participation was as low as it is today. To best answer this question, 50 college level students, who are taught by the authors, were taught using four different learning strategies. The first strategy was called Explore First, where the teachers gave them
certain tasks and allowed them to complete these tasks on their own. The second strategy, Peer Learning, allowed the students to learn from their teacher while also working in groups to help each other understand the material better. The Networking strategy was similar to the first strategy, but involved working in groups instead of individually. The Game Based strategy had students utilizing interactive games in order to learn classroom material. In the end, the students were given a questionnaire regarding the use of the learning strategies used. Game Based and Peer Learning were seen as the most effective by the students because it made them more willing to show up to class and engage themselves in the topic. - What information does this source contribute to your research question?
This source proves that students are most engaged in school when they are allowed to learn their own way and at their own pace, which are both aspects of active learning. - How does the source relate to other sources in your bibliography?
Just like in the previous source, active learning strategies are shown to be a major motivator in student engagement - What are the strengths and weaknesses of the source?
The use of multiple different strategies in this study allows the authors to truly understand what it is about active learning strategies that engage students. Unfortunately, the sample size is too small to be able to give significant results. - How does the source fit into your research topic? Why is it useful?
This source simplifies the question of why active learning strategies are important by highlighting which ones are favored among students.
Research Paper 2
- Team member evaluation:
Jaiden DeBoe - Citation for the article:
Diepreye, Fapohunda and Odukoya, Jonathan. “The Impact of Passive and Active Teaching Methods on Students’ Learning Among Secondary School Students in Yenagoa, Bayelsa State”. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2019, vol. 1378, issue 2. The Impact of Passive and Active Teaching Methods on Students’ Learning Among Secondary School Students in Yenagoa, Bayelsa State – IOPscience - 1-paragraph summary:
The authors of the study gathered 196 high-school-level students in Yenagoa, Nigeria, 72 boys and 124 girls, and had them taught biology topics using four different methods. These methods consisted of practical teaching, class discussions, traditional lectures, and video watching. Afterwards, the students were tested on these topics using the same test. On average, the students who were taught using practical teaching or class discussions scored between 84% and 85% on the test, while students who were taught
using traditional lectures or videos scored between 61% and 70%. - What information does this source contribute to your research question?
Passive teaching methods that involve teachers simply “reading words” to students negatively impact their school performance, while active methods that allow students to learn for themselves allow
them to perform better on tests. - How does the source relate to other sources in your bibliography?
This source connects to our second review paper because they both demonstrate how active learning strategies can be better for comprehension and retention of knowledge. - What are the strengths and weaknesses of the source?
The large sample size of this source does allow for accurate data. However, the difference in numbers between boys and girls could cause the results to be less accurate for the average student. - How does the source fit into your research topic? Why is it useful?
Once again, active learning methods are shown to be more effective in increasing school performance. This specific source highlights this idea in a high-school-level course.
Research Paper 3
- Team member evaluation:
Sonia Sheryr - Citation for the article:
Singh Minhas, Paras et al. “The effects of passive and active learning on student preference and performance in an undergraduate basic science course”. American Association for Anatomy, 20 March 2012, vol. 5, issue 4. The effects of passive and active learning on student preference and performance in an undergraduate basic science course – Minhas – 2012 – Anatomical Sciences Education – Wiley Online Library - 1-paragraph summary:
72 students in a college animal physiology course had their class split into two sessions, a normal lecture from a professor and a peer-led seminar. After each class, the students were asked to rate the efficiency of the teaching method. This study lasted for 2 years, where in the end, the students’ interest in peer-led seminars and their exam scores both increased. 68% of the students in the study argued that implementing active learning strategies along with passive learning strategies would be most effective for
them. - What information does this source contribute to your research question?
Active learning strategies, such as peer-led seminars, are an important part of a student’s education. However, they are most effective when coupled with traditional passive learning strategies - How does the source relate to other sources in your bibliography?
Similar to our first review article, this source shows that the use of hybrid learning strategies is most favored among college students. - What are the strengths and weaknesses of the source? The length of time used in this study allows for multiple assessments on the efficiency of the learning strategies used, which gives the students enough time to consider whether or not these methods are effective long term. The only main downfall of this study is the small sample size.
- How does the source fit into your research topic? Why is it useful?
The authors of this source show how important active learning strategies are for student engagement and performance.
Research Paper 4
- Team member evaluation:
Jaiden DeBoe - Citation for the article:
Mikolaj, Christy. “Effective Instructional Strategies in Sixth Grade Inclusion Mathematics Classrooms: The Effect of Active and Passive Engagement on Concept Learning and Opportunity to Learn”. ProQuest, December 2019. Effective Instructional Strategies in Sixth Grade Inclusion Mathematics Classrooms: The Effect of Active and Passive Engagement on Concept Learning and Opportunity to Learn – ProQuest - 1-paragraph summary:
Taking place in a classroom setting designed to teach 6th-grade students with special needs, six students were taught using a normal lecture method while four students were taught using a project-based method. 23 students who did not require special needs education were also placed in the lecture group,
and 17 other students who did not require special needs education were placed in the project-based group as well. After four days of tests and surveys, the researchers found unexpected results. While students
who did not have special needs performed better when learning using project-based methods, students who did have special needs performed slightly worse when using project-based methods. - What information does this source contribute to your research question?
On average, active learning strategies can positively impact student performance. However, not every student is able to learn the same. Many students require a mix of active and passive learning strategies, while some students may require primarily passive learning strategies. - How does the source relate to other sources in your bibliography?
This source relates to my second review article, because it shows that many students are not able to perform well in school because the education system is unable to match their individual needs. - What are the strengths and weaknesses of the source? The split of students between active learning methods and passive learning methods makes the results more distinct. The bad part about this source is that the small length of time and unproportional representation of special needs students make the results less accurate.
- How does the source fit into your research topic? Why is it useful?
This source supports the idea that hybrid methods could be the best way to teach every student in a way that benefits them individually.
Research Paper 5
- Team member evaluation:
Sonia Sheryr - Citation for the article:
Haidet, Paul et al. “A Controlled Trial of Active Versus Passive Learning Strategies in a Large Group Setting”. Springer Nature, March 2004, vol. 9, pages 15-27. A Controlled Trial of Active Versus Passive Learning Strategies in a Large Group Setting | Advances in Health Sciences Education - 1-paragraph summary:
Residents at a medical institution were given an after-hours teaching session. During this time, the first group were taught in a teacher-student manner, while the second group was taught in a student-student manner. After surveying the residents before and after the sessions, the researchers
determined that both teaching methods led to increased test scores. The only differences were that the first group appeared more engaged and that the second group valued the sessions more. - What information does this source contribute to your research question?
This source supports the idea that active learning strategies can increase student engagement while also arguing that both active and passive methods are equally important in student education. - How does the source relate to other sources in your bibliography?
This source best relates to the idea that hybrid learning strategies are more effective than just active learning strategies, similar to my first review article. - What are the strengths and weaknesses of the source?
Surveying the students right before the session, right after the session, and weeks after the session allows the researchers to measure student perception and student retention. Unfortunately, since this study is only conducted during after-hour sessions, it is difficult to determine whether or not their increase in knowledge is primarily due to these sessions. - How does the source fit into your research topic? Why is it useful?
This source also demonstrates the importance of using both active and passive learning strategies, instead of just one or the other.
Research Paper 6
- Team member evaluation:
Jaiden DeBoe - Citation for the article:
Mahmood, Muhammad et al. “STRATEGIES FOR ACTIVE LEARNING: AN
ALTERNATIVE TO PASSIVE LEARNING”. SAVAP International, November 2011, vol. 1, issue 3. Microsoft Word – 2011_1.3-20_ - 1-paragraph summary: This relates to the issue of learning and offers strategies for active
learning as an alternative to passive learning. Passive learning does not always give a real understanding. While active learning lets students engage by participating and can improve motivation and interest. Active learning is more enjoyable by being hands on and where the student can retain more knowledge. - What information does this source contribute to your research question?
It directly compares active and passive learning correlates to student engagement. - How does the source relate to other sources in your bibliography?
This source best relates to the idea that active learning strategies are more effective than passive learning
strategies, similar to the first review article. - What are the strengths and weaknesses of the source?
Strengths are that it clarifies what they measure regarding student engagement such as interest, motivation, autonomy, and anxiety making it useful to relate it to our variables. Also, they provided qualitative data and multiple strategies that show how active learning can be implemented. Unfortunately only 20 students participated, and the study only lasted a week, so it doesn’t relate to long term. - How does the source fit into your research topic? Why is it useful?
This source relates to active and passive learning strategies and measures how each affects student engagement. It provides us with evidence that active learning strategies is more effective than passive learning such as lecturing.
Science Communication Paper 1
- Team member evaluation: Sonia Sheryr
- Citation for the article: Murgel, M., et al. “Science Communication Project: Articulating
Teaching.” Journal of Chemical Education, vol. 102, no. 1, 2025, pp. 88–96. American Chemical Society, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.4c01569 - 1-paragraph summary:
This was focused to improve students’ understanding of concepts, communication skills, and engagement. Results showed students had a deeper grasp of the material, gained more motivation, and confidence in explaining concepts in clear and detailed ways. These findings highlight how active learning strategies left students with a deeper understanding of concepts by connecting them to real-life situations. - What information does this source contribute to your research question?
This source focuses on how active learning influences the students’ understanding on a deeper level. - How does the source relate to other sources in your bibliography?
This relates to paper 6, regarding active vs learning strategies in a classroom; and relates to several other sources along the same lines as well. - What are the strengths and weaknesses of the source?
This source emphasizes student engagement with active learning which relates to our topic. This relates to
one student topic, but not for long term engagement. - How does the source fit into your research topic? Why is it useful?
This describes how active vs passive methods affect engagement, this paper provides an example of students actively communicating science.
Science Communication Paper 2
- Team member evaluation: Jaiden DeBoe
- Citation for the article: Shivni, R., Martinez, A., & Green, A. (2021). Establishing a baseline of science communication skills in an undergraduate environmental science course. International Journal of STEM Education, 8(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-021-00304-0
- 1-paragraph summary: This source showed that while many students could explain the topics, they
often struggled to adapt themes or clear concepts. The authors suggest that structured, active communication tasks in science classrooms can help students develop stronger engagement and public communication abilities. - What information does this source contribute to your research question?
This source contributes directly to our research question because it establishes that active learning helps students develop stronger engagement and retention. - How does the source relate to other sources in your bibliography?
This relates to research paper 6 where the authors suggest active learning over passive. - What are the strengths and weaknesses of the source?
This focused on a real environment, but it was conducted with a small group. Also, this relies on qualitative data over quantitative. - How does the source fit into your research topic? Why is it useful? This talks about active engagement in environmental education which relates to my focus on active vs passive learning. It is useful to show that hands on learning experiences promote a sharper understanding on students and their overall retention.